Digital Health Tools Archives - Digital Health Age
Digital Health Tools Archives - Digital Health Age unknown
The landscape of healthcare is undergoing a transformative shift, one where the boundaries of physical clinics and hospitals are expanding into the vast expanse of the digital realm. This metamorphosis, known as telemedicine, is not just a change in the mode of delivery but a revolution in how we perceive and access healthcare.
Central to this transformation is the hardware that acts as the bridge between the tactile world of medicine and the virtual corridors of the internet. Understanding what hardware to use is pivotal if you are interested in starting a telemedicine practice.
Now, let us talk about the most important pieces of hardware used in telemedicine.
The Background
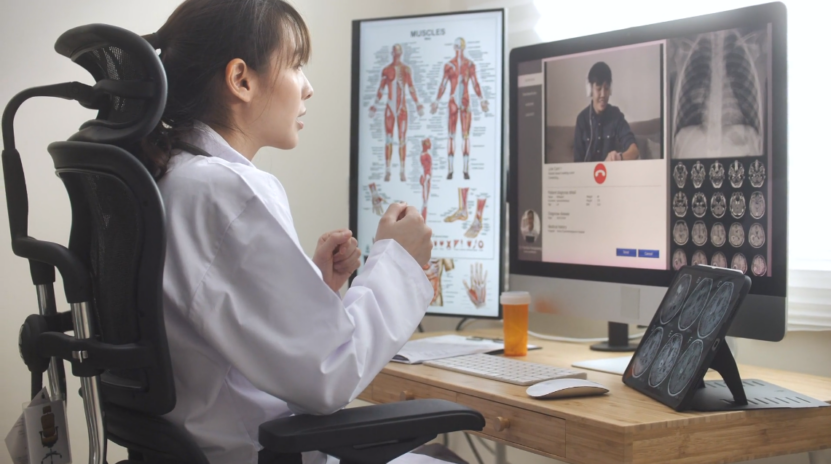
From the rudimentary tools used by ancient civilizations, like bone needles and herbal concoctions, to the sophisticated MRI machines and robotic surgical instruments of today, medical tools have seen a remarkable evolution.
Each advancement has been a testament to humanity’s relentless pursuit of better healthcare, aiming to increase longevity and improve the quality of life.
The Birth of Telemedicine
Even though it may sound strange, humanity celebrates one hundred years of telemedicine these days. Initial endeavors, often using rudimentary video conferencing systems or basic telephone lines, were groundbreaking but had their limitations in terms of video quality, connectivity, and user experience.
These pioneering efforts set the stage for the sophisticated, user-friendly telemedicine platforms we have today.
Essential Hardware for Telemedicine
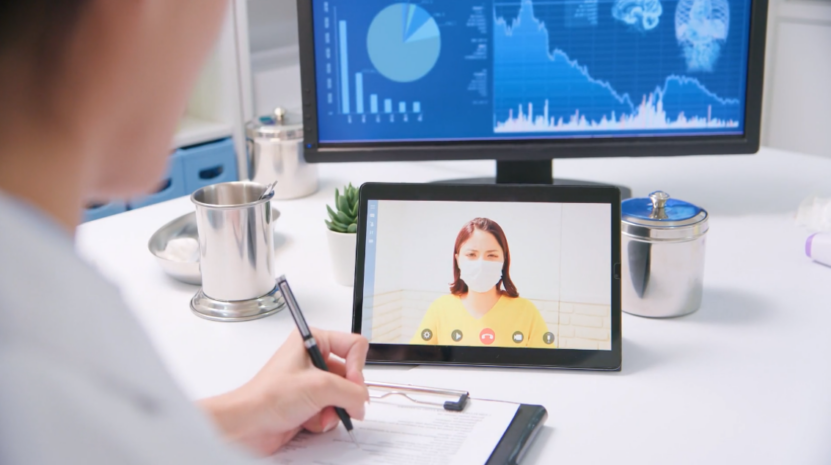

Now that we went through the basics, we want to discuss the most important pieces of hardware used for telemedicine.
Communication Devices
- Computers, laptops, and tablets: These aren’t just screens; they are gateways to virtual clinics. Their evolving processing power and versatility have made real-time consultations, data sharing, and remote diagnostics possible.
- Smartphones and smart devices: The ubiquity of mobile devices has democratized access to healthcare, ensuring that even those in remote locations can seek expert advice.
- Microphones and headphones: These tools, often overlooked, are vital. They ensure that voice clarity is maintained, making consultations effective.
Visual Equipment
- High-definition cameras: The devil is in the details, especially in healthcare. High-definition cameras can capture and relay intricate details, ensuring that doctors don’t miss out on any critical signs.
- Webcams: These devices, often integrated into our computers and phones, have made face-to-face consultations possible, humanizing the virtual experience.
- Portable diagnostic cameras: In specialties like dermatology, these cameras can magnify skin areas, allowing doctors to diagnose conditions that might be invisible to the naked eye.
Medical Devices
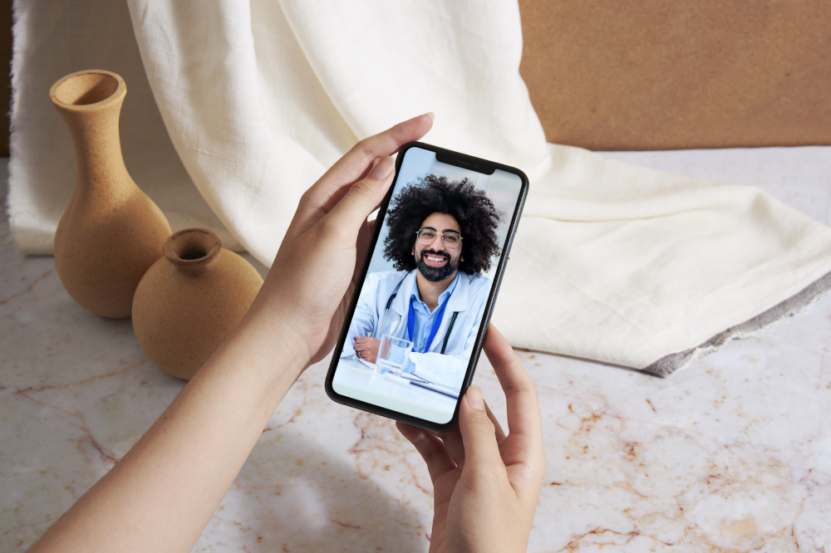

- Digital stethoscopes: These modern marvels can amplify body sounds and transmit them over vast distances, ensuring that doctors can perform auditory examinations remotely.
- Electronic health monitors: Devices that can continuously monitor vital signs like blood pressure, glucose levels, and heart rhythms, and then transmit this data in real-time, are revolutionizing chronic disease management.
- Wearable health trackers: These devices, often worn as watches or bands, collect a plethora of health data, from steps taken to hours slept, providing a comprehensive picture of an individual’s lifestyle and health.
Connectivity Tools
- Routers and modems: These unsung heroes ensure uninterrupted connectivity, which is the backbone of any telemedicine setup.
- Secure VPNs and encryption devices: In a world where data breaches are frequent, these tools safeguard sensitive patient information, ensuring trust in telemedicine platforms.
- Bandwidth and speed considerations: Just as a doctor’s instruments need to be sharp, the internet connection needs to be swift and stable. A lag or disconnection can disrupt consultations, making reliable connectivity paramount.
Hardware for Specific Medical Fields

As you can presume, specific hardware is used for particular medical fields.
Dermatology
| Dermatology | |
|---|---|
| High-resolution imaging devices | Skin conditions often require a detailed examination. These devices can capture high-resolution images, ensuring accurate diagnoses. |
| Skin scanners | Advanced devices that can detect minute changes in skin texture, color, or moisture, aiding in early detection of potential issues |
Cardiology
| Cardiology | |
|---|---|
| ECG monitors | Monitoring heart rhythms is crucial in cardiology. Modern, portable ECG devices, lightweight and portable, can transmit data in real-time, ensuring patients are always monitored. |
| Portable ultrasound devices | These devices allow for on-the-spot imaging of the heart, ensuring that expert care is delivered without delay. |
Mental Health
| Mental Health | |
|---|---|
| VR headsets for immersive therapy | Virtual reality is opening new frontiers in therapy. Whether it’s helping Whether it’s helping PTSD patients confront triggers in a controlled environment or aiding in relaxation techniques, VR is quite effective. |
| Biofeedback devices | These devices, by providing real-time feedback on physiological functions, empower patients to control and improve their mental states. |
Physical Therapy
| Physical Therapy | |
|---|---|
| Motion capture devices | By tracking every movement, these devices help therapists understand a patient’s mobility issues better, leading to tailored therapy sessions. |
| Virtual reality setups | Rehabilitation can be tedious. VR setups make it interactive, ensuring patients are engaged and motivated. |
Choosing Hardware for Telemedicine

Compatibility with software platforms: Seamless integration between hardware and software ensures smooth operations, reducing technical glitches.
- Patient ease-of-use: The best technology is user-friendly. Devices need to be intuitive, ensuring that patients of all age groups can use them without frustration.
- Cost-effectiveness and ROI: Healthcare costs are a concern worldwide. Investments in hardware should lead to tangible benefits, both in terms of patient outcomes and financial returns.
- Data security and HIPAA compliance: Protecting patient data isn’t just ethical; it’s also legal. Ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA is non-negotiable.
The Future of Telemedicine Hardware
As we venture further into the 21st century, the future of telemedicine hardware beckons with promises of unprecedented advancements and innovations. The convergence of various technologies is set to redefine the very fabric of telehealth, making it more integrated, efficient, and patient-centric.
One of the most anticipated developments is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning into telemedicine platforms.
These technologies have the potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy, predict patient health trends, and even suggest treatment plans, all in real-time.
Imagine a future where telemedicine platforms, equipped with AI, can instantly analyze patient data, compare it against millions of medical records, and provide immediate insights, making remote consultations as effective, if not more so, than in-person visits.

Another transformative trend is the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare. The proliferation of smart devices, from wearable health trackers to implantable sensors, will provide continuous streams of health data.
This constant flow of information can be integrated into telemedicine platforms, allowing for real-time health monitoring. For patients with chronic conditions, this means that any anomalies or potential health risks can be detected instantly, with the telemedicine system alerting both the patient and the healthcare provider.
This level of continuous care, facilitated by advanced hardware, could drastically reduce hospital readmissions and improve overall patient outcomes.
FAQs
What are biofeedback devices, and how do they assist in mental health telemedicine?
Biofeedback devices provide real-time feedback on physiological functions, empowering patients to understand and control certain aspects of their mental states.
How do motion capture devices benefit tele-physical therapy?
By tracking every movement, these devices offer insights into a patient’s mobility issues, helping therapists devise effective, tailored therapy sessions.
Are there any data security concerns with telemedicine hardware?
Yes, ensuring data protection and compliance with regulations like HIPAA is crucial. Many telemedicine hardware solutions come equipped with security features like encryption to safeguard patient data.
Is the hardware for telemedicine expensive?
Costs can vary based on the sophistication and brand of the hardware. Many solutions are cost-effective, and the return on investment, considering the broader reach and efficiency of telemedicine, is often favorable.
Do patients need specialized hardware at home for telemedicine consultations?
Typically, a device with a camera and microphone, such as a smartphone or computer, is sufficient for most telemedicine consultations. For specific treatments or monitoring, specialized hardware might be recommended.
Closing Thoughts
The transformative power of hardware in telemedicine is undeniable. As we stand on the cusp of further technological revolutions, it’s imperative for the healthcare sector to stay adaptive and forward-thinking.
Embracing these changes will ensure that quality healthcare remains a right, not a privilege, irrespective of geographical boundaries.